“Inspecting” is actual examination of the exchanger
“Evaluating” use data from inspection to plan how and whento clean, repair and replace heat exchanger
The standard approach to solving the problem is;
1.Identify the problem
2.Gather information, including inspection results
3.Analyze the information
4.Formulate conclusions and recommendations
5.Have others check your work
6.Take action
HEAT EXCHANGER INSPECTIONS
1. Initial examination: general visual inspection
STEPS
-
-
2. Destructive examination
Tubes may also be removed from the bundle and split for visual inspection


3.
Should inspect;
-
-
-
-



EFFECT OF FOULING ON THE THERMOHYDRAULIC PERFORMANCE OF HEAT EXCHANGERS

2.
and fouling blocks flow passages; due to these effects, the pressure drop across the heat
exchanger increases.
3.
4.
subsequent processes or will increase the thermal load on the system.
MECHANISMS OF FOULING
1. Particulate fouling
Particulate fouling may be defined as the accumulation of particles suspended in the process streams onto the heat transfer surfaces.
2.
Deposits formed by chemical reactions at the heat transfer surface in which the surface material itself is not a reactant are known as chemical reaction fouling. Polymerization, cracking, and coking of hydrocarbons are prime examples of reaction fouling.
3.
Corrosion fouling is due to the deposition of corrosion products on heat transfer surface. In this category of fouling process, the heat transfer surface material itself reacts to produce corrosion products, which foul the heat transfer surface.
4.
This type of fouling mostly takes place in cooling-water systems, when water-soluble salts, predominantly calcium carbonates, become supersaturated and crystallize on the tube wall to form scaling.
5.
The attachment of microorganisms (bacteria, algae, and fungi) and macro organisms (barnacles, sponges, fishes, seaweed, etc.) on heat transfer surfaces where the cooling water is used in as drawn condition from river, lake, sea and coastal water, etc.
6.
The freezing of a liquid or of higher-melting constituents of a multicomponent solution on a subcooled heat transfer surface include frosting of moisture in the air, freezing of cooling water in low-temperature processes.
CLEANING OF HEAT EXCHANGERS
1.
2.
-Advantages
-Disadvantages
1.
2. Fill and soak cleaning: This may be repeated several times until satisfactory results are achieved. However, this method is limited to small units only.
-Advantages
1. Uniform cleaning and sometimes complete cleaning.
2. Sometimes chemical cleaning is the only possible method.
3. Capable of cleaning inaccessible areas.
4. Moderate cleaning cost and longer intervals between cleaning.
-Disadvantages
1. Chemicals used for cleaning are often hazardous
2. Non-environmental friendly
1.
Cooling-water fouling can be controlled, and in some cases eliminated, by adequately filtering the intake water.
2.
In this method, the instantaneous flow is increased to remove the fouling deposits. This method is particularly applicable to a heat exchanger fouled badly due to the effects of low velocity.
3. Air bumping of heat exchangers
This technique involves the creation of slugs of air, thereby creating localized turbulence as slugs pass through the equipment.
4.
The cleaning effect is achieved by changing the flow direction in the heat exchanger so that the dirt accumulated in the inlet region and the heat exchanging channels is flushed out.
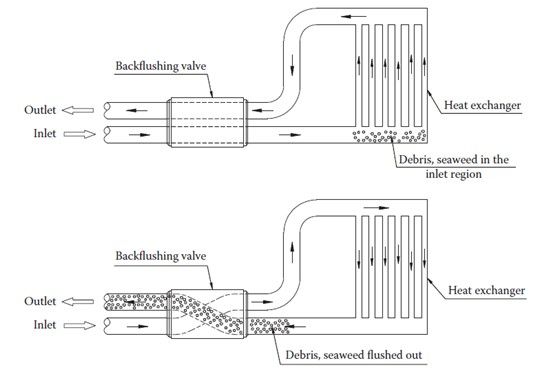
5.
Sponge rubber balls cleaning system: The cooling-water flow forces the balls through the tubes and the deposits on the tube walls are wiped out.

Advantages
1. Extended run time between cleaning intervals
2. Convenient to install
3. Does not require any plant shutdown
4. Can save time and labour
Disadvantage
1. the initial cost may be very high in certain cases.
COST IMPOSED DUE TO FOULING
1.
2. Energy costs
3.
4.
5.
There are two types of leaks in heat exchangers: internal and external. Most time it is from gasket problem. It can cause low pressure drop because not all the flow is entering the tubes that should. And leakage problem is worst in high pressure condition.
Proper venting is a startup necessity. Improper venting usually occurs on startup and is recognized by poor heat transfer and a high pressure drop.
Case study
Refferences
[1] Maurice Stewart, Oran T. Lewis, Heat Exchanger Equipment Field Manual Common Operating Problems and Practical Solutions, 2013.
[2] Kuppan Thulukkanam, Heat Exchanger Design Handbook Second Edition, 2013.
เข้าสู่ระบบเพื่อแสดงความคิดเห็น
Log in